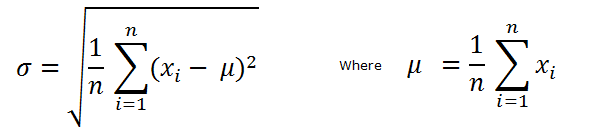
This topic introduces the StandardDeviationCalculator which is part of the Infragistics Math Calculators™ library and explains, with code examples, how to use it to calculate population standard deviation for a set of numbers.
The topic is organized as follows:
Assembly Requirements
Data Requirements
Standard deviation is a measure of dispersion of a data set around the mean. The standard deviation calculation is used to show how much difference there is from the average of values (mean). High value of standard deviation indicates the numbers in a data set are spread out over a large range of values while low standard deviation tells that the numbers tend to be near the mean of the data set.
Standard deviation is computed by taking square root of the sum of squared differences between the variables and the mean (refer to the Infragistics Mean Calculator topic) divided by the total count of numbers in the data set. Also, standard deviation is equal to square root of the variance (refer to the Infragistics Variance Calculator topic) of the set of numbers.
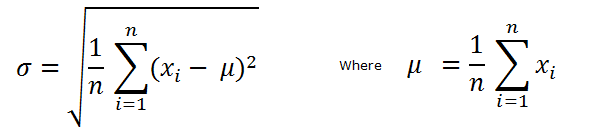
Figure 1 – Formula for Standard Deviation Calculation
This section provides a list of properties of the StandardDeviationCalculator class.
In order to use the StandardDeviationCalculator, the following NuGet package must be added to a WPF project.
Infragistics.WPF.Math.Calculators
For more information on setting up the NuGet feed and adding NuGet packages, you can take a look at the following documentation: NuGet Feeds.
The StandardDeviationCalculator uses ItemsSource property for data binding and ValueMemberPath property for data mapping. Any object that meets the following requirements can be bound to this property:
The data model must implement IEnumerable interface (e.g. List, Collection, Queue, Stack)
The data model must contain items that have at least one numeric data column for calculating the standard deviation.
An example of object that meets above criteria is presented in the following code snippet:
In Visual Basic:
Imports System.Collections.Generic
'...
Public Class DataPointList
Inherits List(Of DataPoint)
Public Sub New(dataValues As IEnumerable(Of Double))
For Each value As Double In dataValues
Me.Add(New DataPoint() With { Key .Value = value })
Next
End Sub
End Class
Public Class DataPoint
Public Property Value() As Double
Get
Return _value
End Get
Set
_value = Value
End Set
End Property
Private _value As Double
End Class
In C#:
using System.Collections.Generic;
//...
public class DataPointList : List<DataPoint>
{
public DataPointList(IEnumerable<double> dataValues)
{
foreach (double value in dataValues)
{
this.Add(new DataPoint { Value = value});
}
}
}
public class DataPoint
{
public double Value { get; set; }
}
This example demonstrates how to calculate standard deviation for a set of numbers using the StandardDeviationCalculator. The StandardDeviationCalculator is a non-visual element and it should be defined in resources section on application, page, control level, or in code-behind, the same way as you would define a data source or a variable. Refer also to the Series Error Bars topic for examples on how to integrate the StandardDeviationCalculator with the xamDataChart™ control in order to calculate error bars for Series objects.
In Visual Basic:
Imports Infragistics.Math.Calculators
'...
Dim data As New DataPointList(New List(Of Double)() From { 5.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 })
Dim calculator As New StandardDeviationCalculator()
calculator.ValueMemberPath = "Value"
calculator.ItemsSource = data
Dim standardDeviation As Double = calculator.Value
In C#:
using Infragistics.Math.Calculators;
//...
DataPointList data = new DataPointList(new List<double> { 5.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0 });
StandardDeviationCalculator calculator = new StandardDeviationCalculator();
calculator.ValueMemberPath = "Value";
calculator.ItemsSource = data;
double standardDeviation = calculator.Value;