xmlns:ig="http://schemas.infragistics.com/xaml"This topic explains how to add the XamBulletGraph™ control to a WPF application.
The following topics are prerequisites to understanding this topic:
To add XamBulletGraph to a page, you need to create an instance of the control and add it to your page’s root element. The control is pre-configured to display a scale with values varying from 0 to 100, major and minor tick marks, and, by default, it takes the size of the container it is placed into.
Add the following NuGet package reference to your main project:
Infragistics.WPF.Gauges
For more information on setting up the NuGet feed and adding NuGet packages, you can take a look at the following documentation: NuGet Feeds.
Also, add the following Infragistics namespaces:
In XAML:
xmlns:ig="http://schemas.infragistics.com/xaml"In C#:
using Infragistics.Controls.Gauges;In VB:
Imports Infragistics.Controls.GaugesFollowing are the general conceptual steps for adding XamBulletGraph.
1. Adding the XamBulletGraph control
2. Configuring the scale
3. Configuring the performance bar
4. Configuring the comparative marker
5. Configuring additional aspects (For details, see Adding XamBulletGraph – Code Example and Configuring XamBulletGraph .)
The following procedure walks through instantiating a XamBulletGraph control, adding it to a WPF application, and configuring a performance bar, comparative measure marker, and three comparative ranges on the scale.
The following screenshot is a preview of the final result.
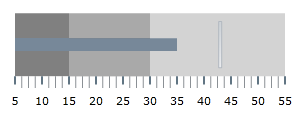
Following is a conceptual overview of the process:
1. Adding the XamBulletGraph control
2. Configuring the scale
3. Configuring the performance bar
4. Configuring the comparative marker
5. Adding comparative ranges
The following steps demonstrate how to add the XamBulletGraph control to an application.
Add a XamBulletGraph declaration to your page’s root Grid element and set its desired Height and Width .
In XAML:
<ig:XamBulletGraph x:Name="bulletGraph"
Height="100"
Width="300">
</ig:XamBulletGraph>In C#:
XamBulletGraph bulletGraph = new XamBulletGraph();
bulletGraph.Height = 100;
bulletGraph.Width = 300;In Visual Basic:
Dim bulletGraph As New XamBulletGraph()
bulletGraph.Height = 100
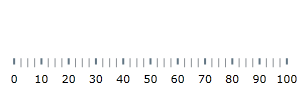
bulletGraph.Width = 300This declaration would instantiate XamBulletGraph with its default look and settings and fixed size. This means that the scale would display the 0÷100 range with major and minor tick marks so it would need some additional configuring.
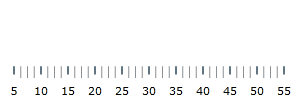
In order to customize the values of the scale, you need to set its MinimumValue and MaximumValue properties . In this example, the scale will start at 5 and end at 55.
In XAML:
<ig:XamBulletGraph x:Name="bulletGraph"
MinimumValue="5"
MaximumValue="55">
</ig:XamBulletGraph>In C#:
bulletGraph.MaximumValue = 55;
bulletGraph.MinimumValue = 5;In Visual Basic:
bulletGraph.MaximumValue = 55
bulletGraph.MinimumValue = 5The changed scale is shown on the following screenshot:
The primary measure of the XamBulletGraph is visualized by its performance bar. Its value is managed by the Value property setting. For this example, set the Value property to 35.
In XAML:
<ig:XamBulletGraph x:Name="bulletGraph"
Value="35">
</ig:XamBulletGraph>In C#:
bulletGraph.Value = 35;In Visual Basic:
bulletGraph.Value = 35The position of the comparative measure marker on the scale is managed by the value of the TargetValue property. For this example, set the TargetValue property to 43.
In XAML:
<ig:XamBulletGraph x:Name="bulletGraph"
TargetValue="43">
</ig:XamBulletGraph>In C#:
bulletGraph.TargetValue = 43;In Visual Basic:
bulletGraph.TargetValue = 43The following screenshot displays what the XamBulletGraph control would look so far in the procedure.
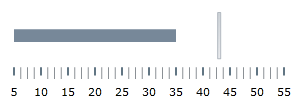
In order to compare the value displayed by the performance bar against some meaningful range(s) of values, these comparative ranges need to be displayed on the scale. Comparative ranges are managed by the Ranges property within which several individual XamLinearGraphRanges can be defined, each of which having its own starting and ending values (StartValue and EndValue) and color (Brush).
For this example, configure 3 comparative ranges, each of a different shade of gray, starting at the 0, 15, and 30 tick marks of the scale, respectively.
In XAML:
<ig:XamBulletGraph x:Name="bulletGraph" >
<ig:XamBulletGraph.Ranges>
<ig:XamLinearGraphRange StartValue="0"
EndValue="15"
Brush="#828181"/>
<ig:XamLinearGraphRange StartValue="15"
EndValue="30"
Brush="#AAAAAA"/>
<ig:XamLinearGraphRange StartValue="30"
EndValue="55"
Brush="#D0D0D0"/>
</ig:XamBulletGraph.Ranges>
</ig:XamBulletGraph>In C#:
XamLinearGraphRange range1 = new XamLinearGraphRange();
range1.StartValue = 0;
range1.EndValue = 15;
range1.Brush = new SolidColorBrush(Color.FromRgb(47, 47, 47));
XamLinearGraphRange range2 = new XamLinearGraphRange();
range2.StartValue = 15;
range2.EndValue = 30;
range2.Brush = new SolidColorBrush(Color.FromRgb(158, 158, 158));
XamLinearGraphRange range3 = new XamLinearGraphRange();
range3.StartValue = 30;
range3.EndValue = 55;
range3.Brush = new SolidColorBrush(Color.FromRgb(198, 198, 198));
bulletGraph.Ranges.Add(range1);
bulletGraph.Ranges.Add(range2);
bulletGraph.Ranges.Add(range3);
bulletGraph.TargetValueBrush = new SolidColorBrush(Color.FromRgb(255, 255, 255));In Visual Basic:
Dim range1 As New XamLinearGraphRange()
range1.StartValue = 0
range1.EndValue = 15
range1.Brush = New SolidColorBrush(Color.FromRgb(47, 47, 47))
Dim range2 As New XamLinearGraphRange()
range2.StartValue = 15
range2.EndValue = 30
range2.Brush = New SolidColorBrush(Color.FromRgb(158, 158, 158))
Dim range3 As New XamLinearGraphRange()
range3.StartValue = 30
range3.EndValue = 55
range3.Brush = New SolidColorBrush(Color.FromRgb(198, 198, 198))
bulletGraph.Ranges.Add(range1)
bulletGraph.Ranges.Add(range2)
bulletGraph.Ranges.Add(range3)
bulletGraph.TargetValueBrush = New SolidColorBrush(Color.FromRgb(255, 255, 255))The final look of the graph is presented below.

The following topics provide additional information related to this topic.